In software development, delivering high-quality, reliable software quickly is crucial. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) have emerged as the recommended practice to achieve this goal. In this blog post, we will explore the concepts of CI/CD, their significance, and how they contribute to the efficiency and success of your software development processes.
Understanding Continuous Integration (CI)
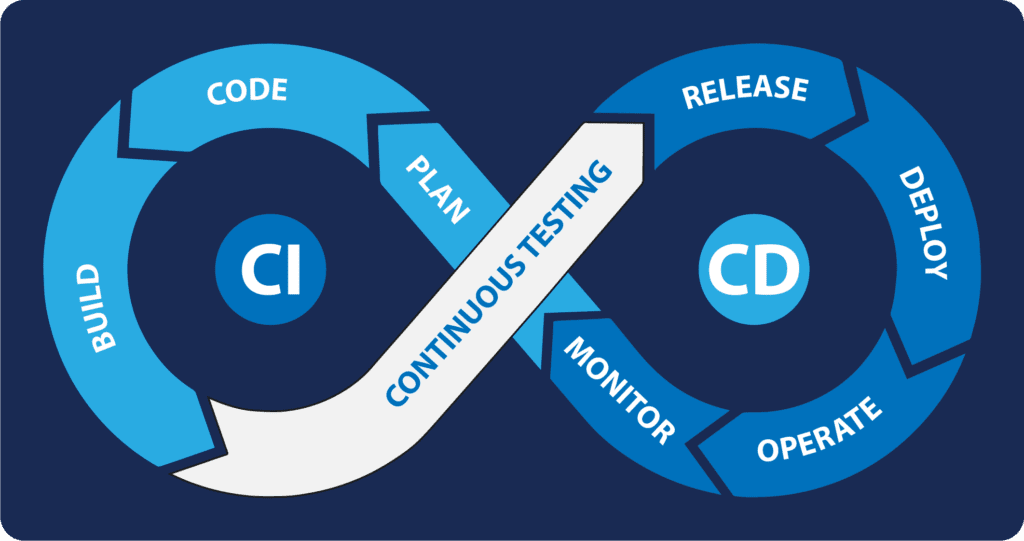
Continuous Integration is a development practice where developers regularly merge their code changes into a shared repository. The primary goal is to detect integration issues early, ensuring that the codebase is continuously integrated and tested. Key aspects of CI include:
- Automated Testing: CI involves running automated tests on the integrated code to identify bugs and issues promptly.
- Frequent Integration: Developers integrate code changes frequently, preventing long-lived branches and reducing the risk of conflicts.
- Version Control: CI relies on version control systems (e.g., Git) to manage code changes and facilitate collaborative development.
Unveiling Continuous Deployment (CD)
Continuous Deployment takes CI a step further by automating the release and deployment of successfully tested code changes to production environments. This ensures a rapid and reliable release process. Key components of CD include:
- Automated Deployment: CD automates the deployment process, eliminating manual intervention and reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuous Deployment often includes monitoring tools to detect issues in production and roll back changes if necessary.
- Incremental Releases: CD supports releasing small, incremental changes, allowing for quicker feedback and easier bug identification.
Benefits of CI/CD
- Early Issue Detection: CI/CD helps catch integration issues and bugs early in the development process.
- Faster Time to Market: Automation reduces manual processes, allowing for quicker and more frequent releases.
- Consistency: CI/CD ensures a consistent and reproducible process for building, testing, and deploying software.
- Reduced Risk: Incremental releases and automated testing reduce the risk of deploying faulty code to production.
Getting Started
There is a fair amount of setup required to get this pipeline in place. This would include investing in a scalable server structure that will allow for different environments and the tools necessary to run the CI/CD pipeline. This also may involve programming costs to create the automated testing scripts. Though there is an up-front cost, the benefit is clear – a proven ROI over time with the reduction of manual processes, as well as a stronger, more quality code base.
Establishing your CI/CD pipeline will build automated checks and balances into the development process and strengthen the scalability of your software.